Ubiquiti Networks is a well-known American producer famous for being the worldwide leader in wireless consumer solutions (20 milion devices sold since 2005). The product line also covers other sector of the telcom world: it’s the case of our reviews’ device, the EdgeRouter X, the basic model of a series of devices dedicated to Routing and Switching that share the EdgeMAX® commercial brand.
EdgeRouter X is an entry-level router aimed to the SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) market with a very aggressive price - price list is 49,99$. Ubiquiti classifies it as a carrier-class product with an advantageous price-performances ratio, and on top of that, a compact metal case.
It comes in two versions:
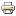
- Edgerouter ER-X, the standard model we tested, can be powered by the included 12V adapter or by 24V PoE on the first Ethernet port. PoE passthrough is available on the last Ethernet port, thus powering devices with passive PoE (it’s not 802.3af standard PoE).
- EdgeRouter ER-X-SFP, which also offers an SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) interface and passive PoE on all five Ethernet ports.
The EdgeOS system
Ubiquiti’s EdgeMax series is equipped with the proprietary system called EdgeOS which includes some important features that we’ll now list.
- VLAN with the 802.1q standard;
- Dynamic routes and Static routes with support for the most common routing protocols such as OSPF, RIP and BGP;
- Guaranteed security with the integrated firewall thanks to the support for NAT rules, ACL and zone-based technology. With the zone-based technology, interfaces are directly assigned to specific zones with analysis rules to be applied on the traffic between zones. Zones define network security perimeters: in practice they define areas where traffic is subject to limitations in case of crossing different zones. By default, traffic between different zones is forbidden;
- Basic services such as DHCP, dynamic DNS, DNS Forwarding and QoS;
- Support for IPv6;
- VPN with IPSec, OpenVPN, PPTP and L2TP.
Management interfaces
In order to “put the hands under the hood” of the EdgeRouter’s configuration, two different options are available: a Web-based interface, to configure main parameters and features and to monitor the device, and a CLI (command-line interface) interface to configure advanced settings.
Initial configuration
The main passages for the basic configuration of the EdgeRouter follow.
- As for every security device, we suggest to download the latest firmware release. Visit downloads.ubnt.com to check if a newer release is available for the EdgeRouter;
- Connect your PC to the eth0 port of the router with an Ethernet cable. Ubiquiti devices have the default IP on the 192.168.1.0 network (and you must have an IP on that network too). In this case, the router’s predefined IP is 192.168.1.1;
- Use your favoured Web browser (preferably FireFox or Chrome) and access to https://192.168.1.1. You’ll be prompted to the configuration interface. Predefined credentials are ubnt both as username and password;
- Before starting the initial configuration, update your device with the latest firmware available: the actual version number used is shown in the left upper corner, right to the EdgeMax logo. Click on the “System” button on the bottom of the dashboard to update your router;
- Inside the System tab, scroll down until you find the “Upgrade System Image” box; upload the image file and start the update process.
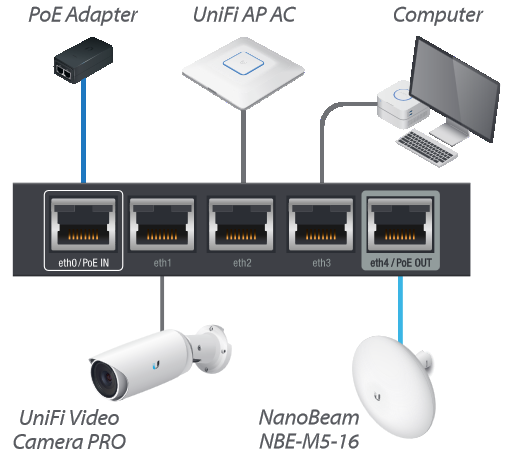
Once the firmware upgrade is done, the installation for a SOHO environments can be carried out with a guided wizard by going on the Wizards tab and selecting one of the predefined templates, shown in the left column. For instance, with the template WAN + 2LAN2 the eth0 interface is used for WAN, while the remaining eth1, eth2, eth3 and eth4 are used for LAN.
The flexibility of the EdgeOS system allows to group ports -admins can decide which ones during the configuration phase- on the same network segment, making them act as if they were part of an integrated switch.
Once a basic configuration is set, all the advanced functions can be enabled, like port forwarding or VPN tunnels.
Example of an advanced configuration
Routing incoming requests on the router’s WAN towards an IP of the internal network is one of the most frequent activities when managing a router or a firewall: for instance you could publish in HTTP on port 81 a Web service running on a machine on the internal network listening on port 80.
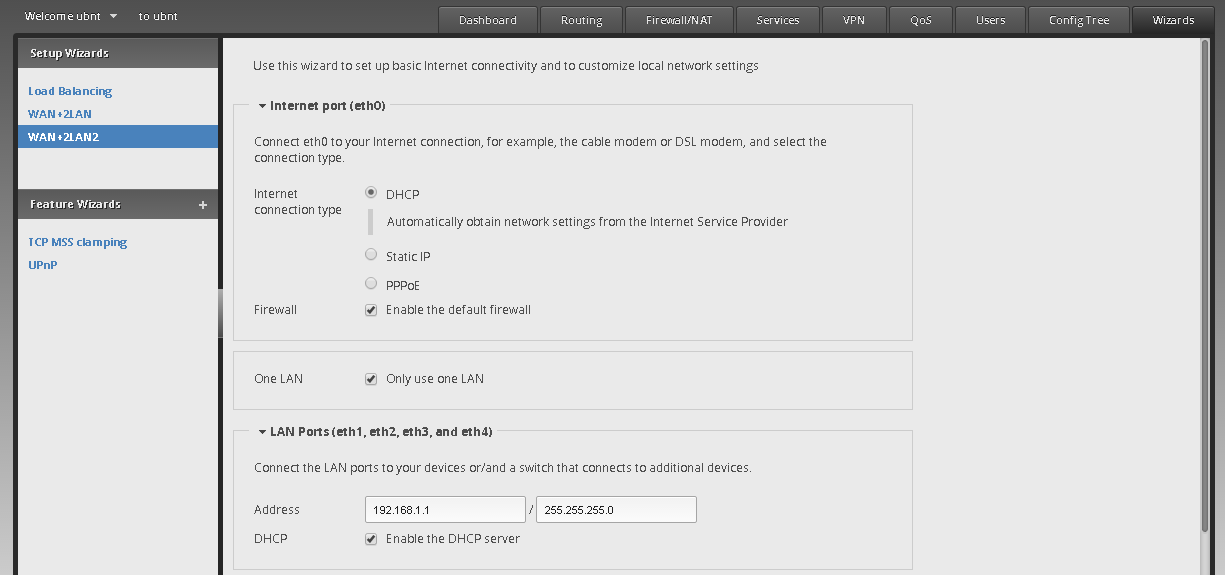
To set such configuration, two distinct steps are required: the first one is creating a firewall rule to allow HTTP requests from any IP to reach the IP of our machine in our LAN. Please note that by default EdgeRouter blocks everything that is not explicitly permitted, which is a policy common to most firewalling devices. The second step concerns a networking part, specifically NAT (Network Address Translation), in which WAN HTTP requests on port 81 are translated on port 80 to the LAN machine.
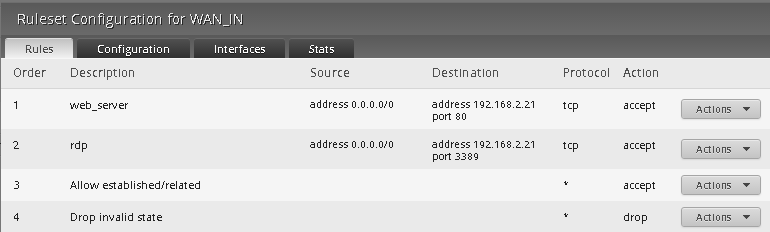
To create a rule, it’s necessary to understand the EdgeRouter logic: rules are grouped in sets called Rulesets, available under the Firewall/NAT tab, then Firewall Policies. You must specify, for each set, the interface that will process packages and the direction of packages themselves, ie incoming or outgoing with respect to the interface. A set contains one or more rules: in our example you will create a rule to accept traffic towards port 80 of the LAN Web server from any IP, as the image below shows:
To create a NAT rule, go to the Firewall/NAT tab, add a new Destination NAT rule and go on with the logic that follows.
- The inbound interface is the interface where packages from the outside come to, so indicate your WAN;
- In the “Translations” tab, specify the machine on your internal network and its listening port (80);
- In “Protocol”, select TCP (which is the transport protocol for HTTP);
- The “Src Address” and “Src Port” must remain empty as the connection can be established by any host on the Internet;
- The “Dest Address” and “Dest Port” fields correspond to the WAN interface that first receives external requests, then specify your WAN’s IP and port 81, which is the one chosen to publish the service;
- Save the rule and start right now to use your Web service from the outside.
Command Line Interface
EdgeOS CLI provides flexible and quick configuration capabilities; it’s suitable for skilled users and allows to control all the advanced features of the EdgeRouter. CLI can be accessed by the serial console port, by SSH or by a dedicated button available in the Web graphical interface.
Menus are hierarchically organized in different levels with a logic that resembles a lot Cisco’s IOS. There are two main levels:
- Operational mode. It’s the first mode available once connected to the device, allowing to see, with limited privileges, some performance data.
- Configuration mode. With this mode you can configure the router. From the “Operational” mode, digit the command “configure” to enter the “Configuration” mode.
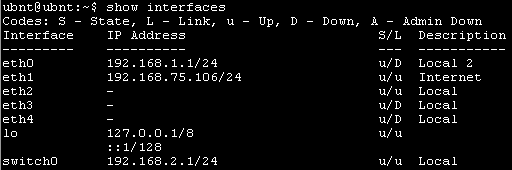
Some useful CLI features: press the ‘?’ character (question mark), a list of commands available within the mode in use will appear. This characters can be also used to understand the parameters of a specific command. For instance, if you write the ‘show’ command followed by the character ‘?’, the list showed below will appear:
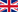
Intuitively, you can easily understand that the command to show interfaces information is “show interfaces”.
What shown is certainly just a bit of what is possible with CLI. Network operators that are comfortable with command line environments know that the control of a device, with such tools, is complete.
Furthermore we remark that some features are available with CLI only. We’re talking about configuring an OpenVPN tunnel, or enabling VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol) to use two routers in High Availability.
Regarding commands sintax, the reference site is Ubiquiti’s Support Center, which can be reached at https://help.ubnt.com/hc/en-us/categories/200321064-EdgeMAX.
Our considerations
The first question that comes up in when dealing with a product like EdgeRouter X is: is a product with enterprise-tier features (as declared) and sold for just 50€ reliable? An answer is possible only with the use in the long run. However, considering the brand, we can make an important consideration: Ubiquiti managed to radically transform the market of outdoor wireless connections through the years. Those niche and only for a few devices, both because of a price reason and for a difficulty of configuration reason, are now within everyone’s reach, enjoying great characteristics, in terms of bandwidth, within prices that are ten time lower than what was available some years ago by renowned brands.
The great price/performance ratio of Ubiquiti’s product allowed several entities to overcome the first obstacle of the digital divide by guaranteeing quality connections with cheap prices. It’s clear that Ubiquiti wants to follow the same path of wifi devices, that is proposing professional and reliable routers with prices of devices found in shopping centres.
EdgeRouter is the ideal device for those who need a security device that is immediate and easy to configure, at least as far as basic features are concerned. Branches and remote offices will take advantage of that. Users with a basic networking knowledge will enjoy it, users that work with networking will be enthusiast of it.
It must be clear that, however, EdgeRouter is not the ADSL router you can find in consumer shops, because it’s not conceived for the domestic use, and it’s not really suited for those who doesn’t know the concepts of IP, network mask, routing and VLAN: from this perspective, some advanced configuration, available with CLI only, will cut out this category of users.