FreeNAS is a FreeBSD-based Operating System whose development began in 2005 thanks to Olivier Cochard-Labbè and whose main function is to transform the computer or server where it’s installed in a NAS (Network Attached Storage). The system was conceived to require a limited use of hardware resource, apart from storage, so that it can run smoothly also on old or performance-wise limited machines.
The development of FreeNAS went on with the years and reached the actual 9.3 stable version and 10 “Alpha” version (the support to the 32-bit UFS file system was abandoned in 2014). In 2009 iXsystems (a company dealing with servers and storage solutions) showed interest in the FreeNAS project in order to avoid the migration of the system on Debian and the subsequent loss to the support for ZFS, after the then project leader. After an important revision and update by the iXsystems’ team, in May 2011 FreeNAS 8.0 was released.
FreeNAS is based on the OpenZFS implementation of the Sun (then Oracle) system called ZFS, so it takes advantage of all the code base of this project to manage ZFS volumes, disks and devices.
Features
The underlying presence of ZFS at the basis of the system allows to use important data protection features like scheduled snapshots, protecting volumes with encryption and both remote and local replica. FreeNAS also allows to share storage on the network using different protocols: NFS, iSCSI Apple AFP and Common Internet File System (CIFS) by Microsoft, including a complete and granular access permissions management. Talking about access permissions, it’s possible to create users and custom groups. Finally, FreeNAS offers configurations with Active Directory, LDAP, NIS, NT4 and Kerberos for those environments where centralized authentication or domain systems are present.
With FreeNAS you can also schedule S.M.A.R.T. tests to check the state of disks -essential given the nature and the main purpose of this Operating System- and send an email to notify possible important events like disks failure, warnings about SMART states and available updates.
A lot of plugins are available, like OwnCloud, Plex Media Server, BitTorrent (Sync) and bacula. However, the use of these plugins adds another layer of difficulty while doing the configuration as it’s required the setup of jails. Jails are an autonomous and isolated environment akin to containers to implement additional software, all done thru command line.
Installation and interface
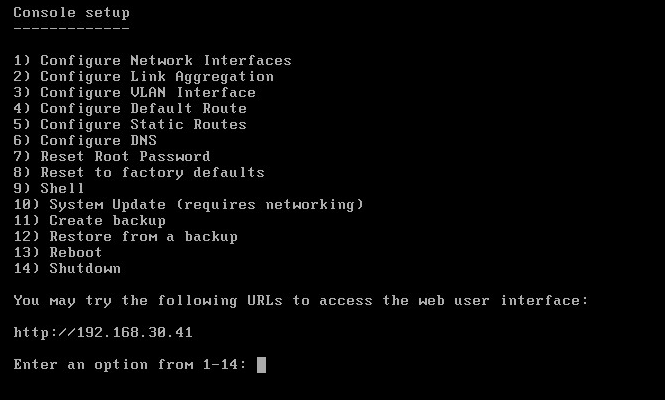
Installation is carried out with a few easy steps and, once completed, a multiple-choice menu is displayed. From here it’s possible to access the basic functions and go on with the initial network configuration.
After the machine is assigned with an IP address (note that FreeNAS also supports VLANs), you can configure the system with the Web-based interface (also reachable via HTTPS).
It’s so possible to set almost every aspect of FreeNAS: there are plenty of functions that require a little bit of a steep learning curve before flawlessly using the product. The upper and the left menu allows to browse the same features, even though the tree organization of the lateral column permits to directly reach voices of the more granular menus.
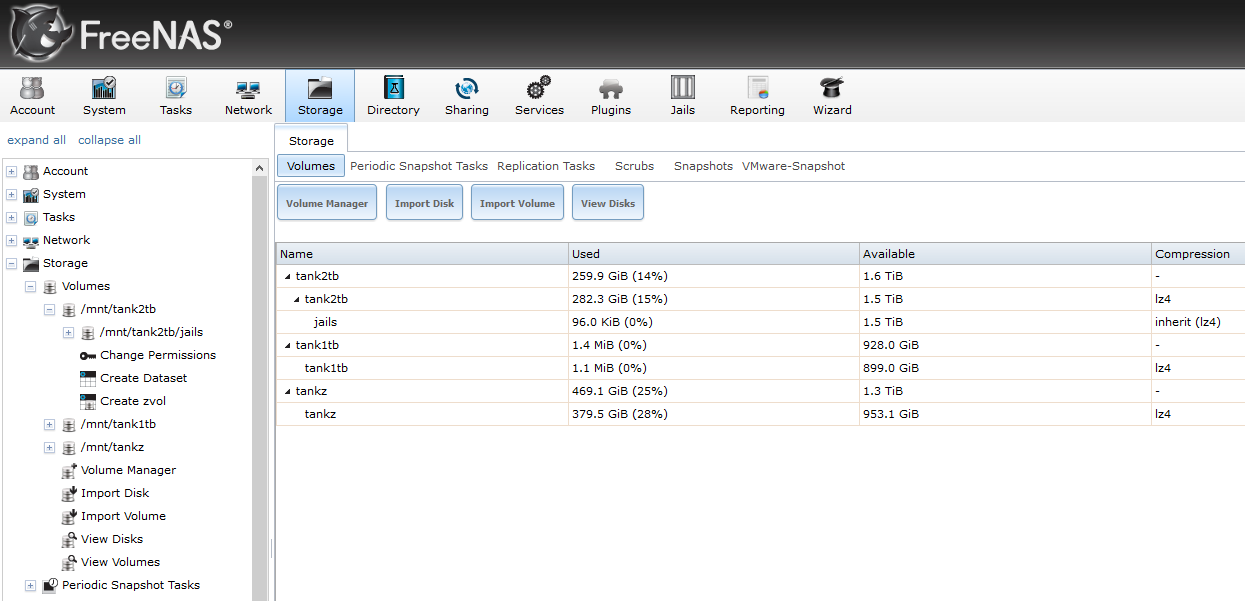
From the storage management area you can see the state of volumes, create new volumes and import volumes with compatible file systems from other systems. This last procedure is particularly easy when using ZFS as all the information on volumes, even multiple-disk volumes, can be read by disks themselves.
It’s a good habit to take note during storage setup of the serial numbers of disks and their positions in the host’s bays, because in case of failures or SMART problems FreeNAS identifies volumes by their serial number (hence the need to know the device-bay association). The comfort of native hardware management offred by RAID controllers is lost.
In FreeNAS Pools (or zpools) are called volumes, while vdev are called device. When creating a volume you can select devices that will compose it starting from available disks. The only way to extend a volume after its creation, as implied by ZFS, is to add other devices. Each device can be configured in Stripe, Mirror, RaidZ1, RaidZ2 and RaidZ3 modes. To better understand these modes we invite you to read the article dedicated to ZFS. You can naturally use spare disks and use one or more disks (SSD recommended) for L2Arc and ZIL to improve reading and writing performances. Once the new volume is created, you can visualize its state, manage permissions, modify settings and create a new zVol or a new dataset. Datasets are the equivalent of a file system inside the file system seen as a sub-directory with an autonomous management of permissions, compression, deduplication and quota management.
zVols are the equivalent of an autonomous raw volume which can be used, for instance, as an iSCSI device to add via network to virtual machines.
The storage section allows to configure Snapshots, replica tasks and data Scrub, which is a process implemented by ZFS itself to analyze data and check integrity on a periodical basis, also correcting identified errors if possible.
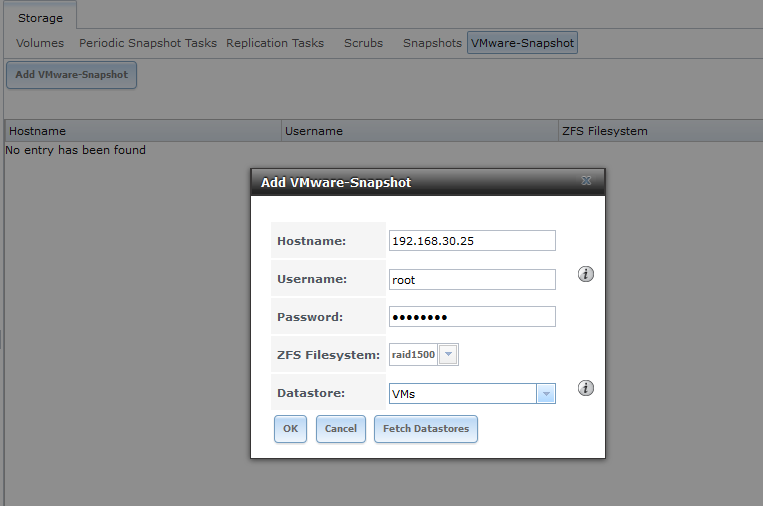
FreeNAS also offers an integration with VMware for snapshots creation: by means of a dedicated feature you can indicate the ESXi host and related datastore to act on (FreeNAS can’t know which is its instance in the list of datastores connected to ESXi). FreeNAS can also create coherent snapshots for each powered-on VM before going on with the overall datastore snapshot. Version 9.3 provided a complete support to VMware VAAI, which are specific APIs to correctly coordinate the two kinds of snapshot.
The part of the interface dedicated to reporting is quite extended and allows to show the instant and the in-time use of resources like CPU, network, memory, ZFS cache and so forth.
Final thoughts
FreeNAS is for sure an interesting product both as a lab solution and in production environments as it’s capable of offering advanced features with an high reliability. The presence of a commercial company like iXsystems developing the system is an added guarantee, other than being a reliable resource if technical support is needed. The product is conceived for the use on physical machines only, nut it can be installed onto a virtual machine without any difficulty. However iXsystem vividly discourages the use in any mode other than bare metal (ie, directly on the hardware).
Amongst the few things that made us to raise our eyebrows is the frequent availability of updates (every one or two weeks). This is naturally positive but -as each update requires a reboot- it’s certainly quite annoying for production devices acting as storages.